Most large organizations now use chatbots to communicate with customers. They’re fast, convenient, and an ideal way to relieve the workload of customer service agents. No wonder the global chatbot market is due to reach $110 billion by 2028.
“The global Chatbot Market Size was worth approx 17.20 USD Billion in 2020 and is predicted to gain revenue of about 110.30 USD Billion by 2028.” (Zion Market Research)
You might have noticed that some bots communicate like automatons while others offer more human-like responses. This brings us to chatbots vs conversational AI.
But wait—aren’t conversational AI and chatbots the same thing? Well, they’re both designed to simulate human conversations and engage in interactions with humans. But in this post, we’ll explore the many differences between these two technologies—and why they matter.
How Chatbots Work
A chatbot is a text-based computer program. It automates specific tasks (often relating to customer service) by replicating human interactions. Artificial intelligence (AI) powers all chatbots, but only some chatbots offer conversational AI.
The most common types of chatbots are rule-based. This means that they follow a set of predefined rules in response to input from a user. Like automated phone menus, these bots use a simple decision tree to match queries with pre-programmed answers.
How Conversational AI Works
Conversational AI uses artificial intelligence to offer more natural interactions with users. Instead of matching user input with a specific keyword, it leverages natural language processing (NLP).
This enables machines to understand and interpret human language. They also generate human-like responses and become smarter over time via machine learning. Conversational AI examples include tools such as Alexa, Siri, and ChatGPT.
Chatbots vs. Conversational AI
The terms “chatbot” and “conversational AI” are often used interchangeably. There is some overlap when it comes to chatbots vs conversational AI, but there are also some important distinctions between them. Let’s discuss both aspects in more detail.
Context-aware interactions
Chatbots follow manual rules
As we mentioned, basic chatbots follow predefined rules. They’re programmed to recognize keywords and phrases that customers might use. They require exact matching to provide an automated output. They don’t understand the context or the intent behind the query, which means that they can gather information but can’t learn new words or develop understanding.

Conversational AI leverages machine learning
Thanks to NLP (a type of machine learning technology), conversational AIs can actually understand the context of a conversation. No matter what words you use to ask a question, they’ll be able to grasp what you mean.
This means users don’t have to repeat themselves or get stuck in a loop. Conversational AI also responds to queries in a natural way, sounding more human than machine.
Interaction complexity
Chatbots handle basic queries
Rule-based chatbots are trained to handle simple questions and provide answers to FAQs—for example, when a customer asks about store opening hours or the company’s returns policy. If a query is more complex, they’ll pass the user on to a human agent. Chatbots can also gather essential information before putting you through to the helpdesk.
Conversational AI excels in diverse interactions
As well as context, conversational AI systems pick up on nuances in user queries. They can detect emotion and sentiment. They understand multiple languages, dialects, and accents. This is because they’re trained on huge sets of data, such as the large language models that power ChatGPT. And the more data they receive, the more intuitive they become.
Improved data-driven methods
Chatbots are programmed with data
Chatbots are capable of picking up certain keywords from user messages. That’s because they’re programmed with answers to common queries. The more data you give them, the more words and phrases they’ll recognize. Extra data improves the bot’s performance, but it’s the programmers who add extra keywords or branches of the decision tree, not the machine itself.
Conversational AI learns from data
Conversational AI continuously learns from data—by itself. It learns from previous inquiries, as well as customer history and transactions. Over time, it becomes more efficient at finding patterns and making predictions. It can also evaluate past interactions to improve and personalize future conversations.
Process versatility
Chatbots have limited capacities
Rule-based chatbots are restricted by the scope of their programming. They can’t respond to anything outside of that. Nor can they handle complex inquiries. If a user asks two questions in one message, the bot may only answer one of them. Chatbots on different channels are likely to operate separately, leading to disconnected experiences.
Conversational AI applies across industries and tasks
Conversational AI can understand more complex queries, including those containing several questions or topics. It also features voice recognition capabilities. This makes it versatile enough for use in a wide range of tasks and across platforms.
Natural sounding responses
Chatbots offer functional interactions
Rule-based chatbots are convenient for basic interactions. But they’re only able to give concise and functional responses. Customers will probably realize they’re communicating with a machine, though they won’t mind if the bot is able to help!
Conversational AI delivers naturally
The idea with conversational AI is that users can’t tell whether they’re talking to a bot or a human. Instead of a scripted conversational flow, conversational AI can deliver more natural responses. And because it understands sentiment and tone, it can even display empathy.
Chatbots and conversational AI in action
To better understand the topic “chatbots vs conversational AI”, it can help to take a look at a few examples of how these technologies can be used across various industries. Let’s dive in.
Retailer chatbot assistants for enhanced shopping experiences
As we mentioned earlier, rule-based chatbots can answer simple questions, such as those about store opening hours or return policies. They’ll also help with tracking orders and sending delivery updates. They can do so by pulling in information you get from your order management software.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, acts as a virtual shopping assistant. It provides personalized product recommendations based on preferences and purchase history.
By telling you exactly what the current trends are for a specific product or customer segment, you’ll be able to feed fresh, accurate information into business-critical solutions such as your CRM platform.
In turn, this will enable you to offer better, faster, and more personalized service, thus boosting the overall experience and satisfaction of your customers.
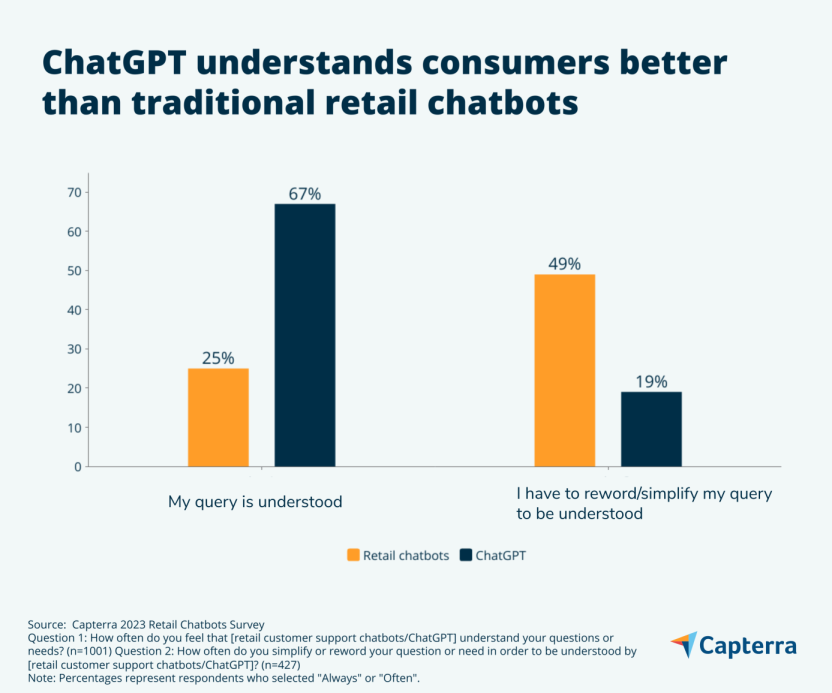
Banking and finance AI for data management and analytics
Again, chatbots handle the simple stuff. Customers use them to view their account balance or check their credit score. In contrast, conversational AI can give personalized financial guidance. (think of Bank of America’s virtual assistant “Erica”, for example.) It also detects fraud by identifying anomalies in user behavior.
Customer support chatbots and virtual helpdesks
Chatbots are a boon for customer support teams. They reduce call queues by handling routine queries such as password resets. They can also gather basic information before passing the customer on to a human, saving time.
Conversational AI may be able to resolve a more complex query without having to bring in a human, although in some cases, this kind of intervention is necessary. If this happens, you could consider integrating your advanced conversational ai solution with your time and expense management software.
This will enable you to keep a close eye on how your customer support team is performing in terms of swiftly responding to queries and providing excellent service while also ensuring every agent is compensated fairly for the amount of work they do.
Healthcare AI assistants for patient interaction
Chatbots can gather basic patient data, which helps healthcare professionals improve patient experiences.
Online AI assistants, on the other hand, can ask about symptoms and medical history before scheduling appointments. In a physical setting, they can collect relevant information when patients arrive and create a triage system for prioritizing urgent patients.
Conversational AI tools in healthcare can be connected to the provider’s main electronic health records system, which may help to speed up appointment scheduling, streamline clinical workflows, and empower patients to take better control of their health.
Key Takeaways
When discussing conversational ai vs chatbot, it can be all too easy to talk about the similarities of these two technologies: the differences, though, do matter. Let’s have a quick recap of conversational ai vs chatbot:
- Rule-based chatbots respond to common questions with pre-programmed answers
- They can’t grasp context or learn from data
- Conversational AI uses NLP to understand context and intent
- It learns continuously and becomes smarter over time.
That’s why conversational AI is better for complex inquiries and human-like interactions. Both technologies are useful for data-gathering, but conversational AI delivers more actionable insights and a smoother customer experience.